ASHRAE wraps up first hybrid Winter Conference
ATLANTA, Georgia, 4 February 2022: More than 2,800 HVACR industry professionals, building systems engineers, architects, contractors and students gathered in Las Vegas and virtually from January 29 to February 2 for the 2022 ASHRAE Winter Conference, ASHRAE said through a Press release. Registered conference attendees received entry to the co-sponsored AHR Expo, held from January 31 to February 2 at the Las Vegas Convention Center, ASHRAE added.
“This year’s Conference and Expo marked the first time that the Society has been together for our Winter Conference in two years and the return to the AHR Expo after last year’s cancellation,” said Mick Schwedler, 2021-22 ASHRAE President. “While the numbers are expectedly lower than past conferences, in-person attendance still exceeded our expectations, and our virtual attendees added a welcomed dynamic to our sessions. We are grateful to everyone involved in establishing a comprehensive health and safety plan for our attendees, which included guidance provided by the ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force.”
According to ASHRAE, the Winter Conference featured over 50 technical sessions, updates from Society leaders, tours, social events and livestreamed sessions for virtual attendees. Top sessions included Introduction of Building Decarbonization, HVAC Design, Control and Operation of Hospitals After COVID-19 Fiasco and CPS 21: Refining ASHRAE COVID Guidelines and Standard 100, ASHRAE said.
According to ASHRAE, the AHR Expo offered a total of 1,573 exhibitors, with 281 international exhibitors, occupying 443,769 square feet of exhibit space in the Las Vegas Convention Center. More than 43,000 people pre-registered to attend the show, including 130 media representatives, ASHRAE said.
At the Winter Conference, Schwedler provided updates related to the Society’s current theme, “Personal Growth. Global Impact. Feed the Roots”, ASHRAE said. He focused on personal development and how the Society’s extraordinary global growth and impact to the built environment has nourished the roots of the global HVACR industry, ASHRAE added.
“When we concentrate on our mission and vision and talk about our impacts – we make the world more sustainable and resilient to future changes,” Schwedler said. “We reduce both energy utilization intensity and environmental emissions. We helped mitigate a global pandemic by keeping vaccines cold – and their efficacy high – 40% of the world’s food spoils between the field and consumption. We reduce that. And most importantly, we keep students and staff in schools, and occupants of the built environment safe and healthy.”
During the plenary session of the Conference, Jeff Littleton, Executive Vice President and Secretary, ASHRAE, reported on the Society’s current initiatives, as well as the dedication of ASHRAE volunteers during the pandemic. “A Diversity, Equity and Inclusion Board subcommittee is focused on proactively driving diversity, equity and inclusion at all levels of the Society,” Littleton said. “Task groups have been formed to drive Society strategies on decarbonization and on international standards. We’ve released 14 new and 24 revised publications and standards.
Examples of new publications include the ASHRAE Design Guide for Natural Ventilation and the ASHRAE Guide for HVAC in Hazardous Spaces. We’ve even released the children’s book, Lucy’s Engineering Adventure. The commitment of ASHRAE’s entire global membership to the Society’s work has never wavered during the pandemic. I find that truly remarkable. When so much of our professional and personal lives has been disrupted, some 7,000 ASHRAE volunteers at the society, regional and chapter levels continue to drive ASHRAE forward.”
ASHRAE said an honors and awards ceremony, tied to the Conference, was an occasion for recognizing experienced and emerging leaders in the industry. Record-breaking polar explorer, Ann Daniels, closed the plenary session with an inspiring presentation on good leadership, teamwork and self-belief.
The ASHRAE Learning Institute (ALI) offered 17 courses. According to ASHRAE, new courses were as follows: Advanced High-Performance Building Designs: Key Concepts for Lifelong Building Sustainability; V in HVAC – What, Why, Where, How, and How Much (includes Basic Requirements of Standard 62.1-2019); Best Practices for Installing DDC Systems; Save 40% by Complying with Standard 90.1-2019; Principles of Building Commissioning: ASHRAE Guideline 0 and Standard 202; Guideline 36: Best in Class HVAC Control Sequences; Changing Environments and Loads for Data Centers (High Density, Liquid Cooling, Edge Computing); and Health Impacts of Indoor Air Extraction, Ventilation, and Filtration – Same or Different.
ASHRAE said all registered attendees, both in-person and virtual, would have access to the virtual conference environment for 12 months, post-conference. Registration, the Society said, is still open for access to the virtual conference until January 2023 at ashrae.org/2022winter.
ASHRAE said the 2022 ASHRAE Annual Conference will take place from June 25 to June 29 in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The 2023 Winter Conference will take place from February 4 to 8, and the AHR Expo, from February 6 to 8, in Atlanta, Georgia.
Camfil donates air purifiers to Pertini
STOCKHOLM, Sweden, 15th June 2021: Camfil Italy in Cinisello Balsamo donated air purifiers to the municipality for the Il Pertini Cultural Center, Camfil said through a Press release, adding that it was a gesture of generosity and attention to the city, in which it has been operating for the last 46 years. The air purifiers, the company said, have been placed in the study room in one of the buildings, which has become an important step as many young students and professionals spend hours studying there.
Following an inspection, Camfil proposed the installation of three air purifiers in the study room. The clean air solutions, capable of purifying the air from pollen, bacteria, viruses, particulate matter, ozone, chemicals and other harmful contaminants, are also the same adopted by the French and Spanish regional authorities in the canteens, laboratories, and study rooms of their schools, Camfil said. Silent and with very low energy consumption, the City M air purification systems will guarantee about 16 changes per day of purified air, thanks to HEPA H14 filters, with a certified filtration efficiency of 99.995% even on the smallest particles in the air, it added.

Luciano Rogato, Managing Director, Camfil Italy, said: “We are humbled to have donated three air purifiers to the reading room of the Pertini Cultural Center, which plays a central role in promoting culture, socialization, and creativity in the Cinisello Balsamo community. It is an important contribution, as the local communities and public places have remained under strict restrictions due to the pandemic. Our clean air solutions ensure a healthy and safe indoor environment.”
Mayor Giacomo Ghilardi, said: “I thank Camfil for this donation to our city library, which is a hub for so many young people for studying, reading, and as a meeting place. Due to the health emergency, which is still ongoing, the Pertini was closed for some time, and we know how much discomfort this has created for many students and young professionals. The installation of these machines will allow more comfortable and healthy use of the indoor environments.”
Camfil launches CamCarb VG engineered molecular filtration solution
STOCKHOLM, Sweden, 12 May 2021: Camfil launched the CamCarb VG engineered molecular filtration solution, which the company described as a robust solution suited for make-up air and recirculation air systems. The primary use of the technology, Camfil said, is the control of acidic gases that are responsible for the corrosion of electronics and electrical equipment in heavy process industries, such as pulp and paper mills; petrochemical refineries; mining and metal refining operations; and wastewater treatment plants. They are also suitable for lighter applications, such as the removal of noxious and odorous fumes generated outside airports, hospital helipads, cultural heritage buildings, and commercial offices located in city centres, Camfil added. The modules can be filled with different types of Camfil molecular filtration media to suit the specific customer application, the company said. There are two standard configurations of CamCarb VG: VG300 and VG440, it said, adding that the VG300 format is best suited for moderate duty (normally make-up air) applications, and the VG440 is best suited for light-duty (recirculation air) applications.

According to Camfil, CamCarb VG filters can be installed in specially designed housings, with options for front-loading, side-loading, or positive-seal side access (PSSA). They can also be used as replacements in housings and track systems produced by other manufacturers, the company said.
The modules are fully welded and constructed without adhesive to eliminate the possibility of off-gassing, Camfil said. They include a unique moulded mesh to allow the use of a full range of loose-fill media without shedding, it said. Many applications will require multiple molecular media to address a range of contaminants. The different media should be deployed in a series of layered modules. This layered approach will provide the highest removal efficiency, the longest life, and the lowest total cost of ownership (TCO), as each media can be changed when it reaches the end of its useful life, it said, adding that a blended-media, on the other hand, requires all the media to be replaced when just a single component has failed.
ASHRAE supports USGBC IAQ schools survey and report
ATLANTA, Georgia, 29 April 2021: With technical support from ASHRAE, the Center for Green Schools at the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) published a new report on indoor air quality (IAQ) measures that schools have taken in response to the pandemic, ASHRAE said through a Press release.
The report, titled “Preparation in the Pandemic: How Schools Implemented Air Quality Measures to Protect Occupants from COVID-19”, presents the survey responses of school districts representing more than 4,000 schools serving over 2.5 million students in 24 states, on the protocols and operations plans implemented to mitigate the spread of COVID-19.
“Maintaining proper ventilation and good indoor air quality are vital in keeping school buildings healthy and operating as energy efficiently as possible,” said 2020-21 ASHRAE President Charles E. Gulledge III. “This report provides a wide-scale, foundational framework to school leaders and lawmakers alike towards the implementation of new building design guidelines and to advance health and sustainability goals, while instilling confidence in the places where people learn.”
According to ASHRAE, the report is the only known national view of air quality measures implemented in schools during the pandemic. It highlights what school districts have prioritized, which actions they have taken, how they have made decisions and what the consequences have been. The results of the survey show that schools have implemented some protective measures to improve IAQ, prioritizing ventilation and filtration to reduce the transmission of the virus, ASHRAE said. However, school districts still have unmet needs and face numerous challenges related to costs and outdated building infrastructure, ASHRAE added.
“Indoor air quality continues to be a critical concern as more teachers and students are returning to the classroom,” said Anisa Heming, Director of the Center for Green Schools, USGBC. “Increasing clean air circulation for our teachers and students is vital to promoting public health and is a key green building strategy for school buildings. Our aim with this report is to inform policymakers and nonprofits that support our schools of the challenges that our education institutions face in combatting the spread of COVID-19, particularly given the deficient state of many school buildings across the country.”
Additional findings from the survey include:
- The most-frequently-cited challenge to implementing protective air quality measures at schools was that school buildings were not designed to support the strategies that were being recommended.
- School districts that have been able to act have leaned heavily on their mechanical systems, such as increasing air supply through HVAC systems or upgrading filters to implement protective air quality measures for students and teachers.
- Only two-thirds of respondents were regularly monitoring IAQ before the pandemic, indicating that providing time, staff and funding for regular monitoring and data collection has not been a priority for many districts in the past.
- Respondents want to continue the measures implemented during the pandemic, citing student and teacher health. Seventy per cent of school districts plan to continue some or all of the strategies they have implemented.
“As schools re-open and develop health and safety plans to mitigate airborne transmission of COVID-19, many are prioritizing and upgrading current HVAC systems to provide the highest indoor air quality for building occupants,” said Corey Metzger, Lead, ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force Schools Team. “We know that improved indoor air quality has a positive impact on student performance and general well-being, and I’m hopeful that more schools will consider and implement the guidance provided by ASHRAE.”
ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force releases updated Building Readiness Guide
ATLANTA, Georgia, 02 February 2021: With the performance of many HVAC systems in buildings still being evaluated, the ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force has updated its reopening guidance for HVAC systems to help mitigate the transmission of SARS-CoV-2, ASHRAE said through a Press release.
“The Building Readiness Guide includes additional information and clarifications to assist designers and commissioning providers in performing pre- or post-occupancy flush calculations to reduce the time and energy to clear spaces of contaminants between occupancy periods,” said Wade Conlan, Lead, ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force Building Readiness team. “New information includes the theory behind the use of equivalent outdoor air supply, method for calculating the performance of filters and air cleaners in series, and filter droplet nuclei efficiency that help evaluate the systems’ ability to flush the building.”
According to ASHRAE, major updates to the building readiness guidance include the following:
- Pre- or post-flushing strategy methodology: The strategy has been updated to include the use of filter droplet nuclei efficiency, which is the overall efficiency of filter, based on viable virus particle sizes in the air, to assist in determining the impact of the filter on the recirculated air on the equivalent outdoor air. This allows the filter efficiency as a function of particle size, using ASHRAE Standard 52.2 test results, to be estimated based on the expected size distribution of virus-containing particles in the air. This calculation is currently based on Influenza A data and will be updated as peer-reviewed research becomes available for the distribution of particle sizes that contain a viable SARS-CoV-2 virus. Additionally, a chart has been added to help determine the time to achieve 90%, 95% or 99% contaminant reduction, if the equivalent outdoor air changes per hour is known.
- Flushing time calculator: There is now a link to a view-only Google Sheet that can be downloaded for use, to help determine the available equivalent outdoor air changes and time to perform the flush. This sheet is based on a typical mixed AHU with filters, cooling coil, with potential for in-AHU air cleaner (UVC is noted in the example), and in-room air cleaning devices. Provided efficiencies of MERV-rated filters are based on the performance of over 200 actual filters from MERV 4 through 16, but the tool also allows users to enter custom characteristics for specific filters.
- The sheet also calculates the filter droplet nuclei efficiency, based on the cited research but allows a user to adjust the anticipated distribution of virus, as desired. It also allows specification of the zone (room) air distribution effectiveness from ASHRAE Standard 62.1 to account for the impact of the HVAC system air delivery method on the degree of mixing. Default calculations assume perfect mixing. Finally, the tool allows for the target air changes to be adjusted if an owner wants to achieve a different per cent removal in lieu of the recommended 95%.
- Heating season guidance: The guide now includes data to consider for heating of outdoor air and the potential impact on pre-heat coils in systems.
- Adjustments to align with Core Recommendations: The Core Recommendations were released in January 2021, and this guidance document needed to be updated to ensure that the information provided aligned with the intent of those recommendations. This included minimum outdoor air supply and filter efficiency requirements and their role in an equivalent outdoor air supply-based risk mitigation strategy.
According to ASHRAE, the guidance still addresses the tactical commissioning and systems analysis needed to develop a Building Readiness Plan, increased filtration, air cleaning strategies, domestic and plumbing water systems, and overall improvements to a system’s ability to mitigate virus transmission.
ASHRAE releases core recommendations for reducing airborne infectious aerosol exposure
ATLANTA, Georgia, 14 January 2021: The ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force has released new guidance to address control of airborne infectious aerosol exposure and recommendations for communities of faith buildings, ASHRAE said through a Press release.
An infectious aerosol is a suspension in air of fine particles or droplets containing pathogens, such as the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which can cause infections when inhaled, ASHRAE said. They can be produced by breathing, talking, sneezing and other as well as by flushing toilets and by certain medical and dental procedures, it added.
ASHRAE’s Core Recommendations for Reducing Airborne Infectious Aerosol Exposure concisely summarize the main points found in the detailed guidance documents produced by the ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force, it said. They are based on the concept that ventilation, filtration and air cleaners can be combined flexibly to achieve exposure reduction goals, subject to constraints that may include comfort, energy use and costs, it added.
“This guidance outlines a clear approach for lessening the risk of infectious aerosol exposure for building occupants that can be applied in a wide range of applications, from homes to offices, to mobile environments, such as vehicles and ships,” said William Bahnfleth, Chair, ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force. “ASHRAE’s Core Recommendations are based on an equivalent clean air supply approach that allows the effects of filters, air cleaners, and other removal mechanisms to be added together to achieve an exposure reduction target.”
According to ASHRAE, specific recommendations include the following:
- Public health guidance
- Follow all regulatory and statutory requirements and recommendations.
- Ventilation, filtration, air cleaning
- Outdoor airflow rates guidance for ventilation, as specified by applicable codes and standards.
- Recommendations on filters and air cleaners that achieve MERV 13 or better levels of performance.
- The use of air cleaners.
- Control options that provide desired exposure reduction while minimizing associated energy penalties.
- Air distribution.
- Promote the mixing of space air.
- HVAC system operation
- Maintain temperature and humidity design set points.
- Maintain equivalent clean air supply required for design occupancy.
- Operate systems for a time required to achieve three air changes of equivalent clean air supply.
- Limit re-entry of contaminated air.
- System commissioning
- Verify that HVAC systems are functioning as designed.
According to ASHRAE, the task force’s Communities of Faith Buildings guidance offers recommendations on conducting worship services under epidemic conditions.
Rick Karg, ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force member, said: “The intent of the Communities of Faith guidance is to offer those who operate and care for buildings used for worship a plan for implementing short- and long-term HVAC strategies to reduce the possibilities of transmission of the SARS-CoV2-2 virus. The document also helps communities move toward a new ‘normal’ operation after this public health emergency nears an end.”
According to ASHRAE, recommendations for Communities of Faith include the following:
- Identify HVAC system characteristics. Compile and review operation and maintenance manuals and schedules.
- Verify HVAC systems are well maintained and operating as intended. For maintenance, follow the requirements of ASHRAE Standard 180 – 2018, Standard Practice for the Inspection and Maintenance of Commercial HVAC Systems.
- Consider PPE when maintaining HVAC systems, including filters, coils and drain pans.
- Operate HVAC systems, if present, with system fan set to run continuously when building is occupied for services or cleaning.
- Operate the system for a time required to achieve three equivalent air changes of outdoor air (effect of outdoor air, filtration and air cleaners) before the first daily occupancy and between occupied periods, if appropriate. Three equivalent air changes can be calculated using ASHRAE’s Building Readiness Guide.
To view the complete ASHRAE Core Recommendations For Reducing Airborne Infectious Aerosol Exposure and Communities of Faith Building guidance, ASHRAE suggested visiting ashrae.org/COVID-19.
ASHRAE Learning Institute opens registration for Spring online courses
ATLANTA, Georgia, 8 January 2021: ASHRAE Learning Institute announced that registration is open for its 2021 Spring online instructor-led course series. The 16 online offerings, including eight new courses, run from January through June, the Institute said
A new course, ‘Reopening Commercial Buildings: Evaluating Your HVAC System’s Readiness to Mitigate the Spread of SARS-CoV-2’, taking place on January 27, will expound the online ASHRAE COVID-19 details for reopening buildings and the Building Readiness Plan for HVAC systems, the Institute said. The course will help reiterate mitigation strategies available and understand specific buildings arrangements, the Institute added.
The course, ‘Health Impacts of Indoor Air Extraction, Ventilation, and Filtration – Same or Different’, scheduled for February 17, the Institute said, will cover the future design of forced air ventilation systems and the most cost-effective HVAC operational changes and system modifications to improve existing indoor environments in reducing the spread of viruses.
The course, ‘Hospital HVAC – Infection Mitigation, Comfort, Performance’, scheduled for February 23, will address the role of HVAC systems in helping to reduce Hospital Associated Infections (HAI), explaining airborne versus contact transmission, the Institute said. This course will describe the why and how filtration, air patterns, air changes, dilution, temperature, humidity, UV and pressurization in hospital HVAC can either help or hinder efforts to reduce HAI, the Institute added.
According to the Institute, the following is the full schedule of online instructor-led course offerings:
January 26: COVID-19 and Buildings: Re-occupation after Lockdown
January 27: Reopening Commercial Buildings: Evaluating Your HVAC System’s Readiness to Mitigate the Spread of SARS-CoV-2
February 17: Health Impacts of Indoor Air Extraction, Ventilation, and Filtration – Same or Different?
February 23: Hospital HVAC – Infection Mitigation, Comfort, Performance
February 24: Evaluating Your HVAC System’s Readiness to Mitigate the Spread of SARS-CoV-2
March 2: Latest in High-Performance Dedicated Outdoor Air Systems
March 4: Humidity Control I: Design Tips and Traps
March 25: Save 40% by Complying with Standard 90.1-2019
April 6: Commercial Building Energy Audits – Part I
April 13: Commercial Building Energy Audits – Part II
April 20: Air-to-Air Energy Recovery Fundamentals
April 22: V in HVAC – What, Why, Where, How, and How Much
May 4: An Introduction to ASHRAE Existing Building Commissioning
May 11: Fundamentals of Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI) for Air and Surface Disinfection
May 20: Introduction to BACnet
June 1: Principles of Building Commissioning: ASHRAE Guideline 0 and Standard 202
June 8: Powering with Renewable Resources: Thermal Energy Storage
Climate change and the larger picture of finances

Mayor James Brainard
Q&A: James Brainard, Mayor of Carmel, Indiana, United States
We have succeeded admirably in our fight against the depletion of the ozone layer through collective effort, through a cohesive, consensus-based approach of finding economically and technically sound alternatives to ozone-depleting refrigerants. How much confidence do you take from what has been a marvellous example of social cooperation?
We did the summit in the form of the Montreal Protocol over concerns of huge spike in cancer deaths, so it was a great example of world leaders coming together to study a problem, devise a solution and then go back to their countries to fix the problem. It shows diplomacy and recognition of common challenges can be good.
In the same way, could we not find a financially feasible, well-structured long-term plan to curb the widespread misuse of energy and general profligacy through steady and substantial investment in the infrastructure needed to achieve the goal?
You have identified the problem in the question, and we have to find the means of accomplishing this. We have to look at the larger picture of finances – the health impact of pollution; the cost of famines; the cost of relocation, if we have a rise in sea level, leading to the displacement of people from major cities; and the cost of possible conflicts arising out of this. But more specifically, we need to recognize many jobs are dependent on the fossil fuel industry. So, we can make those changes, but we have to recognize that we need to look out for investment of industry, we still need to fly airplanes. But, we have a saying in the US, ‘low- hanging fruit’. So, there are many easy things we can do to clean the environment and reduce fossil fuel use, and those are what we can focus on with recognising that we have to protect people’s jobs in the fossil fuel industry and that many are invested in the fossil fuel industry.
Would an approach of self-financing the fight against global warming by developing an energy budget in every city, town, state and country across the world be a possible way out, as propounded by George Berbari, the CEO of DC Pro Engineering? I am referring to a structured, long-term carrot-and-stick approach, where individuals and organisations occupying residential and commercial buildings could be rewarded for being energy efficient and penalised for being inefficient, with the penalty being slightly higher than the reward to create a positive budget, a surplus, which could be used for giving rebates to homeowners for improving insulation, glazing, etc., for developing infrastructure to lower primary energy use, for building thermal energy networks, even District Energy schemes… anything that would effectively fight climate change.
I think it would help. The colloquial shotgun approach, where we undertake to do a lot of small things. I think your idea of financial incentives and disincentives is good; and tied to that what needs to happen is disincentives need to increase over time and incentives need to go up and come down. It is certainly a system we need today. You could still pass laws, where each year, the incentives and disincentives change, to encourage disincentives to go up and incentives to go away. The tax system is also there. Or, it could be a separate tax, a carbon tax, and it has been discussed here since the late 1980s.
Economists believe such an approach to conserving primary energy is feasible, but democratically elected local and federal government leaders and local mayors have limited terms and, generally speaking, give priority to short-term problems, the solving of which gives them immediate political benefits, as opposed to decades-long and daunting task of curbing energy use through a financial mechanism and other initiatives, which might also be viewed by the city’s inhabitants that make the electorate, as adding to existing costs and impairing their personal and corporate competitiveness. In your case, you are one of the longest-serving mayors in the state, having been in office since 1996 over seven consecutive terms. Did that give you a canvas to paint a long-term vision? How effective was the approach? Did it help you shape regulation and enforcement at a city level? Were you able to raise greater awareness on the human impact on climate change and bring about a consensus-based change in energy use behaviour in Carmel?
We are a suburb of Indianapolis, which has a population of two million people. We are 100,000 people in Carmel. Now, places like Dubai and Doha require automobiles, owing to the urban sprawl. Generally, we need the automobile to go anywhere. We have looked at the problem and have a series of PPPs, where one can live, work, go to restaurant and engage in recreational activities without having to get into an automobile and, as a result, lower the consumption of fuel.
The average American spends two hours a day in automobiles, but in Carmel, businesses, houses, schools are all here. We have adopted land use development differently, so people can live, work and go to a restaurant all in the same area, and we tried to design our downtown not for automobiles, and it has cut down fuel use. In Carmel, it is 15 minutes to half an hour of automobile use per person, so it is much, much less [than the national average].
We have a legal structure in the state of Indiana that makes decisions on building codes, and they have done less than what I would like to see, but we have contract to have a much more efficient build. We have the example of the Energy Center in Carmel. We have cold winters and hot summers in Carmel, and we are using energy all year long to either heat or cool our buildings. And if you have an individual heating or cooling system, it starts and stops and is energy inefficient. And so, we have developed the Energy Center in the city, and it uses 50% less energy. And we would like to see this being applied across the city.
If energy is scarce and its excessive use damaging to the environment, should people be allowed to consume as much as they want to, as long as they are paying for it? Should affordability be a sole factor? Could we change that mindset and, at the same time, take care not to infringe on personal freedom and quality of life?
I have thought about it, and I believe in a capitalistic and free market approach. And there is a way to fix it, which is you pay USD 10, say, for 100 units of use, USD 15 for the next 100 units, and USD 20 for the next 100 units. And so the more you use, the higher the price. And it is a good system, because it penalizes the people to use it, and at the same time, they have the freedom to use it. In the case of steel production, maybe that may be very important for the economy and jobs, and so there should be a different model. You have to look at the situation where we can improve the environment, decrease carbon and increase quality of life.
Have you established a carbon neutrality goal for Carmel, like Copenhagen, for instance, where we are seeing a consensus-based approach involving all political parties, underpinned by the thought process that environmental action needs to be bipartisan in nature? Or are the political dynamics different in the United States?
It’s a good question. Our city is mainly Republican, and is fiscally and economically conservative. Some years ago, a seven-member council introduced a carbon neutrality goal, which is not mandated, however. We know we will get there, because the technology is there. It is not time bound. It is a legislative body that passed a law that laid out a carbon neutrality goal.
We have been measuring progress in reducing carbon. Every year, we are measuring how much energy the city is using on a per capita basis, because the city is growing. I don’t know if we have done enough yet, but we are making progress. I firmly believe technology will save us.
The fight against climate change needs to be a non-partisan effort within cities, states and nations. What we have seen is a vastly polarising view within the United States. With Joe Biden set to take the reins, how soon can we expect to see the United States aligning itself in a more profound manner to the Paris Agreement?
I am a Republican, and my undergraduate degree was in history, so I tend to think not today but historically. At the turn of the century, Ted Roosevelt, a Republican, set aside millions of acres in the US for the National Parks system. And President Eisenhower in 1952 established the Arctic Reserve in Alaska, and he was Republican, as well. And President Nixon was the one who set up the federal EPA. Republicans signed a law that amended our Clean Water Act. They passed a whole series of environmental laws. President Reagan led on the Montreal Protocol for the ozone protection initiative. George HW Bush and George Bush came from a state that produces a lot of oil, and yet they established a system of hundreds of windmills. Over 120 years, Republicans and Democrats have come together in a non-partisan manner. And they will come back; this anomaly has been only for a sort period of time. Clean air and water are non-partisan issues. Disagreement will come only in terms of jobs.
On December 11, 2020, the United States observed a new daily death record of 3,055 individuals, more than the number of people who died in Pearl Harbour or the September 11 attacks on the twin towers in New York City. The coronavirus cases have risen sharply in Carmel, as they have elsewhere in Indiana and across the country. What measures have you taken in Carmel to safeguard residents through better indoor air quality (IAQ), with science advocating more fresh air changes and maintaining Relative Humidity between 40% and 60% in buildings?
I think one good thing that has come from the pandemic is recognition of IAQ being important, and there are great many entrepreneurs in the US selling systems that clean the air. Our City Hall operates a new system that every few minutes recycles the air and filters and cleans the air in the building; and it is energy efficient. And building owners throughout the US are adopting this. I see this as a positive thing that has emerged.
I have put a taskforce in Carmel. We also have generated messages through emails and print newsletters and social media. We have used an entire gamut of ways to talk to people, not just about IAQ but also about things to do to handle the pandemic in a better way. Our city had done a good job till the first week of October, testing and quarantining people. It worked through summer, but when people came indoors when the temperatures fell, it went bad. We had our first set of vaccinations, yesterday (the interview with Mayor Brainard took place on December 15), so we hope to be in good shape by March or April 2021.
There are those that are saying building industry stakeholders simply need to reverse the polarity on their thinking when it comes to budgeting for indoor air quality and that we need to raise buildings fit for purpose.
Yes, it’s a good point. Energy for buildings is important, but I think IAQ is something that would work very well. We have tax incentive to make buildings more energy efficient, and over time if building owners do not take action, a penalty would start; and simultaneously, there will be a reduction in taxes for people who make more energy-efficient buildings. And that puts the burden away from the average taxpayer. Yes, I do believe in an incentive and disincentive system for establishing good IAQ.
How to kill enveloped viruses in just 30 minutes
 Poor ventilation in closed indoor environments is associated with increased transmission of respiratory infections. There have been numerous SARS-CoV-2 transmission events associated with closed spaces, including some from pre-symptomatic cases. The role of ventilation in preventing SARS-CoV-2 transmission is not well-defined – that is, by preventing dispersal of infectious particles in small waterdrops to minimise the risk of transmission or preventing transfer of an infectious dose to susceptible individuals.
Poor ventilation in closed indoor environments is associated with increased transmission of respiratory infections. There have been numerous SARS-CoV-2 transmission events associated with closed spaces, including some from pre-symptomatic cases. The role of ventilation in preventing SARS-CoV-2 transmission is not well-defined – that is, by preventing dispersal of infectious particles in small waterdrops to minimise the risk of transmission or preventing transfer of an infectious dose to susceptible individuals.
SARS-CoV-2 is thought to be primarily transmitted through large respiratory droplets; however, an increasing number of outbreak reports implicate the role of aerosols in SARS-CoV-2 outbreaks. Aerosols consist of small droplets and droplet nuclei, which remain in the air for longer than large droplets. Studies indicate that SARS-CoV-2 particles can remain infectious on various materials, such as air conditioning surfaces in air ducts and air handlers, as well as in aerosols in indoor environments, with the duration of infectivity depending on temperature and humidity.
 While HVAC coatings are often the most cost-efficient insurance for the longevity of your air-handling system, there’s much more to them than just increasing your building systems’ lifespan. The rising demand for antimicrobial coatings was triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic and tenants worried about their wellbeing from airborne diseases. In the same category, antimicrobial coatings can make a huge difference for indoor air quality and occupant safety. There are a number of HVAC coatings that drive energy savings, primarily desiccant-coatings.
While HVAC coatings are often the most cost-efficient insurance for the longevity of your air-handling system, there’s much more to them than just increasing your building systems’ lifespan. The rising demand for antimicrobial coatings was triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic and tenants worried about their wellbeing from airborne diseases. In the same category, antimicrobial coatings can make a huge difference for indoor air quality and occupant safety. There are a number of HVAC coatings that drive energy savings, primarily desiccant-coatings.
Found on AHU heat exchangers, coils and in duct systems, they enable recovering heat and moisture, which then helps building owners to save on operational cost. Recent studies have uncovered an extreme antimicrobial effect of desiccant coating systems, in high relative humidity, as present in air conditioning systems. It appears the surfactants can break the exterior protein of a virus or bacteria strain. Once the protein is destroyed, the virus cannot attach to cells and transfer or alter human ribonucleic acid (RNA).
 In many circumstances, once microbes have begun to proliferate on a painted surface, constant cleaning and disinfecting is required to keep growth under control, which is highly unwanted inside an air conditioning system. Recognising that the ability to clean constantly is unreasonable in most air conditioning systems, the best weapon against corrosion and microbial growth is an antimicrobial paint that prevents growth of, or eliminates, bacteria and viruses. Both the coating and the possible active ingredient should not produce any environmental, safety or health issues during application. Any off-gas from the film is unwanted, because ideally, the coating must be applied to air conditioning systems in operation without any concern of release of poisonous additives.
In many circumstances, once microbes have begun to proliferate on a painted surface, constant cleaning and disinfecting is required to keep growth under control, which is highly unwanted inside an air conditioning system. Recognising that the ability to clean constantly is unreasonable in most air conditioning systems, the best weapon against corrosion and microbial growth is an antimicrobial paint that prevents growth of, or eliminates, bacteria and viruses. Both the coating and the possible active ingredient should not produce any environmental, safety or health issues during application. Any off-gas from the film is unwanted, because ideally, the coating must be applied to air conditioning systems in operation without any concern of release of poisonous additives.
Antimicrobial efficacy based on silver ions
Generally, an antimicrobial surface contains an additive, like Agion, which inhibits the antimicrobial property that is composed primarily of silver ions, which have been proven in antimicrobial use throughout history. It incorporates silver ions inside a zeolite carrier, providing an area for these ions to exchange with other positively charged ions – often sodium – from the moisture in the environment.
Once exchanged, these now “free” silver ions are attracted to oppositely charged hydrogen ions, commonly found in most bacteria and microbes. The bacteria and microbes’ respiration and growth are now abruptly halted, since the hydrogen ions are no longer available. Silver based antimicrobial coatings contain a pesticide additive that evaporates slowly from the coating surface and raises questions on the durability of discharge. In Europe and North America, these coatings require a registration by the government authorities.
Antimicrobial efficacy based on desiccation
Enveloped viruses, like the H1N1 influenza virus, Corona (COVID-19) and bacteria have membranes of protein and enzymes to protect the infecting contents. The spreading of the viruses and bacteria in closed spaces and air conditioning systems is carried out by smaller aerosols. Alternative antimicrobial functionality is based on desiccation, a physical process to extract the moisture from the virus and bacteria particles. This approach may seem relatively primitive; however, it is extremely effective in slowing down or even preventing microbes from spreading and transmission. This method is similar to other physical treatments, such as UV irradiation, filtering and heating.
 Desiccant coatings inactivate a wide variety of microbes that adhere to the surface through their hydrophilic surface properties. The antiviral functionality of the coating has been tested on the Phi6 virus, which is commonly used as surrogate for enveloped Corona viruses.
Desiccant coatings inactivate a wide variety of microbes that adhere to the surface through their hydrophilic surface properties. The antiviral functionality of the coating has been tested on the Phi6 virus, which is commonly used as surrogate for enveloped Corona viruses.
Studies
A recent study shows that a desiccant coating can have an extremely quick kill-rate of enveloped viruses after just 30 minutes.
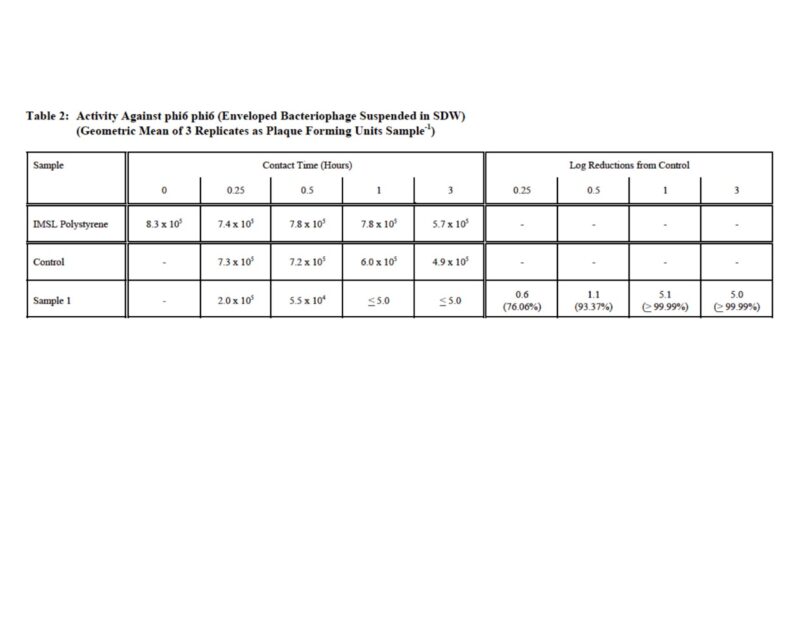 Further studies have proven that strong antimicrobial working was additionally confirmed. Surface activity results in full kill-rates of > 99,99%, which were confirmed on the following micro-organism strains:
Further studies have proven that strong antimicrobial working was additionally confirmed. Surface activity results in full kill-rates of > 99,99%, which were confirmed on the following micro-organism strains:
- Salmonella
- Legionella
- E-Coli
- MRSA
- Klebsiella Pneumoniae
An important note should be added to this paper: No claim or assertion should be made that the antimicrobial properties in the coating will improve air quality or eliminate the threat of disease-causing microbes in the air supply system. A healthy indoor air system is highly dependent on a combination of design, maintenance and cleaning measurements that are incorporated in the air conditioning system and facility management procedures.
- Knibbs LD, Morawska L, Bell SC, Grzybowski P. Room ventilation and the risk of airborne infection transmission in 3 health care settings within a large teaching hospital. Am J Infect Control. 2011 Dec;39(10):866-72.
- Lu J, Gu J, Li K, Xu C, Su W, Lai Z, et al. COVID-19 Outbreak Associated with Air Conditioning in Restaurant, Guangzhou, China, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Apr 2;26(7).
- Rothe C, Schunk M, Sothmann P, Bretzel G, Froeschl G, Wallrauch C, et al. Transmission of 2019-nCoV Infection from an Asymptomatic Contact in Germany. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 5;382(10):970-1.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Natural Ventilation for Infection Control in Health-Care Settings. 2009 [updated 4 May 2020].
- Ong SWX, Tan YK, Chia PY, Lee TH, Ng OT, Wong MSY, et al. Air, surface environmental, and personal protective equipment contamination by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) from a symptomatic patient. Jama. 2020;323(16):1610-2.
- Bahl P, Doolan C, de Silva C, Chughtai AA, Bourouiba L, MacIntyre CR. Airborne or droplet precautions for health workers treating COVID-19? The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2020.
- Dietz L, Horve PF, Coil DA, Fretz M, Eisen JA, Van Den Wymelenberg K. 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID19) Pandemic: Built Environment Considerations To Reduce Transmission. mSystems. 2020 Apr 7;5(2):e00245-20.
8 Evaluation of Phi6 Persistence and Suitability as an Enveloped Virus Surrogate Aquino de Carvalho, Nathalia; Stachler, Elyse N.; Cimabue, Nicole; Bibby, Kyle Environmental Science & Technology (2017), 51 (15), 8692-8700CODEN: ESTHAG; ISSN:0013-936X. (American Chemical Society)
Recent outbreaks involving enveloped viruses, such as Ebola virus and SARS COVID-2, have raised questions regarding the persistence of enveloped viruses in the water environment. Efforts have been made to find enveloped virus surrogates due to
challenges investigating viruses that require biosafety-level 3 or 4 handling. In this study, the enveloped bacteriophage Phi6 was evaluated as a surrogate for enveloped waterborne viruses. The persistence of Phi6 was tested in aq. conditions chosen based on previously published viral persistence studies. Our results demonstrated that the predicted T90 (time for 90% inactivation) of Phi6 under the 12 evaluated conditions varied from 24 minutes to 117 days depending on temperature, biological activity, and aq. media compn. Phi6 persistence was then compared with persistence values from other enveloped viruses reported in the literature. The apparent suitability of Phi6 as an enveloped virus surrogate was dependent on the temperature and compn. of the media tested. Of evaluated viruses, 33%, including all conditions considered, had T90 values greater than the 95% confidence interval for Phi6. Ultimately, these results highlight the variability of enveloped virus persistence in the environment and the value of working with the virus of interest for environmental persistence studies.
- The use of bacteriophages of the family Cystoviridae as surrogates for H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in persistence and inactivation studies
Adcock, Noreen J.; Rice, Eugene W.; Sivaganesan, Mano; Brown, Justin D.; Stallknecht, David E.; Swayne, David E.
Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A: Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering (2009), 44 (13), 1362-1366CODEN: JATEF9; ISSN:1093-4529. (Taylor & Francis, Inc.)
Two bacteriophages, .vphi.6 and .vphi.8, were investigated as potential surrogates for H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in persistence and chlorine inactivation studies in water. In the persistence studies, .vphi.6 and .vphi.8 remained infectious at least as long as the H5N1 viruses at both 17 and 28 degrees C in fresh water, but results varied in salinated water. The bacteriophage .vphi.6 also exhibited a slightly higher chlorine resistance than that of the H5N1 viruses. Based upon these findings, the bacteriophages may have potential for use as surrogates in persistence and inactivation studies in fresh water.
- Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Persistence and Disinfection of Human Coronaviruses and Their Viral Surrogates in Water and Wastewater, Andrea I. Silverman and Alexandria B. Boehm, April 2020
- Determination of the Antiviral Activity of Water-Based Coating for Air Conditioning Applications against phi6 Bacteriophage using a Method Based on ISO 21702:2019, the laboratories of Industrial Microbiological Services Ltd at Pale Lane Hartley Wintney, Hants, RG27 8DH, UK. December 2020
The writer is with Aqua Aero Coatings and may be contacted at wouter@aquaaero.net
Daikin India acquires Citizen Industries
GURGAON, India, 16 December 2020: Daikin Airconditioning India acquired India-based AHU manufacturer, Citizen Industries through a share-purchase agreement, signed on December 15, the former said through a Press release.
According to Daikin, the acquisition will provide prominence to its current infrastructure influence and help increase its penetration across various applications.
Citizen Industries has two manufacturing units, a big base of R&D engineers and service technicians that Daikin said would complement its people strength. The integration of the two companies, Daikin added, would result in joint sales velocity; acquiring of ongoing air-side maintenance contracts; expansion into the applied and VRV solution business, including air side; a horizontal collaboration with American Air Filter (AAF); and catalysing economies of scale at Daikin’s Neemrana factory in the western Indian state of Rajasthan and its R&D centre.
Daikin said its acquisition of Citizen Industries mirrors its assertive philosophy of identifying opportunities ahead of time and building value around its offerings, while keeping customer requirements at the forefront to create a sustainable business, faster than the rest.


